A Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) VRF system, also known as Variable Refrigerant Volume (VRV) in some regions, is an advanced HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) technology designed to provide efficient and flexible climate control in commercial and residential buildings. It is a ductless system that uses refrigerant as the heat exchange medium to cool or heat indoor spaces.
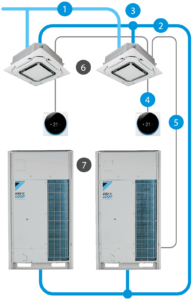
Key features and components of a VRF air conditioning system include:
- Outdoor Unit: The outdoor unit contains a variable speed compressor that can modulate its capacity to match the cooling or heating requirements of the building. This flexibility results in energy efficiency and precise temperature control.
Indoor Units: VRF systems utilize multiple indoor fan coil units that are installed in different zones or rooms. Each indoor unit is individually controlled, allowing for zoned temperature control and reduced energy wastage in unoccupied areas.
Refrigerant Piping: Refrigerant lines connect the outdoor unit to the indoor units, carrying the refrigerant to transfer heat. These lines are typically smaller in diameter than traditional HVAC ductwork, making installation more flexible.
Control System: VRF systems use advanced control systems to manage the operation of both the outdoor and indoor units. These systems can be integrated with building automation systems for centralized control and monitoring.
Heat Recovery: One of the significant advantages of VRF systems is their ability to recover waste heat from cooling processes and redirect it for heating other areas within the building. This heat recovery feature can lead to substantial energy savings.
Zoning: VRF systems are ideal for buildings with varying heating and cooling needs in different areas or rooms. By using individual indoor units and the ability to heat and cool simultaneously, VRF systems provide precise zoning and personalized comfort.
Energy Efficiency: VRF systems are known for their energy efficiency because they adjust the amount of refrigerant flow and compressor speed based on the load, which reduces energy consumption compared to traditional HVAC systems.
Quiet Operation: VRF systems often operate more quietly than conventional HVAC systems, making them suitable for noise-sensitive environments.
Design Flexibility: The absence of ductwork and the small size of indoor units provide greater design flexibility and easier installation in both new construction and retrofit projects.
Eco-Friendly Refrigerants: Many VRF systems use environmentally friendly refrigerants with lower global warming potential (GWP) to reduce their impact on the environment.
VRF air conditioning systems are commonly used in hotels, office buildings, residential complexes, and other applications where efficient, zoned climate control is essential. When properly designed and maintained, they offer energy savings, comfortable indoor environments, and flexible temperature control. However, their initial installation costs can be higher than traditional systems, and the complexity of the technology may require specialized expertise for design and maintenance.
