The four main stages of the refrigeration cycle, also known as the vapor-compression cycle, are:
1.Evaporation: This is where the refrigerant absorbs heat from the environment it’s trying to cool.
2.Compression: The compressor takes the low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant vapor and compresses it into a high-pressure, high-temperature gas.
3.Condensation: The compressed hot gas then passes through the condenser, where it releases heat to the surrounding environment (usually outside air). As it loses heat, the refrigerant changes back into a liquid state.
4.Expansion: The high-pressure liquid refrigerant then passes through an expansion valve (also called a throttle valve or capillary tube). This valve rapidly decreases the pressure of the refrigerant, causing it to expand and cool down significantly.
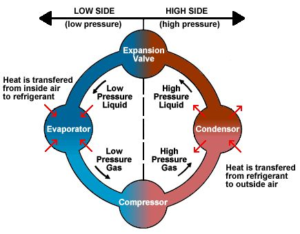
REFRIGERTION CYCLE
Here’s a brief breakdown of each stage:
1. Evaporation:
- The evaporator, located in the area you want to cool (e.g., your refrigerator or room), contains the low-pressure refrigerant.
- The refrigerant absorbs heat from the surrounding air or objects, causing them to cool down.
- As the refrigerant absorbs heat, it evaporates (changes from a liquid to a gas) and becomes even colder.
2. Compression:
- The low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant vapor then enters the compressor.
- The compressor is essentially a pump that increases the pressure of the refrigerant vapor.
- As the pressure increases, the temperature of the refrigerant also increases significantly.
3. Condensation:
- The high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant gas then flows through the condenser, usually located outside the area you want to cool.
- The condenser is typically a series of coils with fins that help transfer heat to the surrounding environment (often with the help of a fan).
- As the hot refrigerant releases heat to the environment, it condenses (changes from a gas back into a liquid) and becomes cooler.
4. Expansion:
- The high-pressure liquid refrigerant from the condenser then passes through an expansion valve.
- This valve acts like a bottleneck, rapidly decreasing the pressure of the refrigerant as it flows through.
- This sudden pressure drop causes the refrigerant to expand rapidly. This expansion process requires energy, which is absorbed by the refrigerant itself, causing it to cool down significantly.
Looking to install a commercial HVAC System or Duct work in your Business Area?
Contact Vipul Ac to learn about our HVAC Service
Call +91 9825636606 Today.


