HVAC design refers to the detailed planning and engineering of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems in a building. It’s a crucial process that ensures occupants’ comfort, health, and energy efficiency within a structure.
Here’s a breakdown of the key aspects of HVAC design:
1. System Selection:
- Considering Building Parameters: The design starts with analyzing the building’s size, usage, insulation levels, and climate.
- Choosing the Right System Type: Based on the analysis, engineers select the most suitable HVAC system type. Common options include:
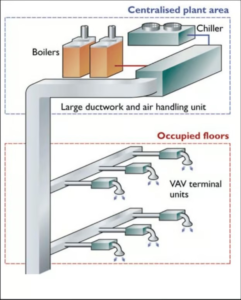
- Centralized Systems: Employ a central furnace or air handler to distribute conditioned air throughout the building using ductwork.
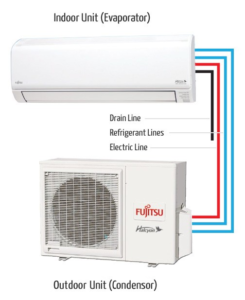
- Split Systems:Consist of separate indoor and outdoor units, providing heating and cooling for specific zones.
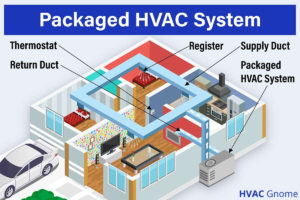
- Packaged Systems:Integrate all HVAC components into a single compact unit, often used in smaller buildings.
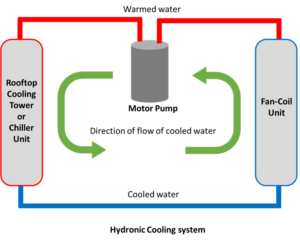
- Hydronic Systems:Utilize hot or chilled water instead of air for temperature control.
2. Load Calculations:
HVAC engineers perform meticulous calculations to determine the heating and cooling loads a building requires. This considers factors like:
- Internal heat gains: Occupants, equipment, and lighting generate heat.
- External heat gains: Solar radiation through windows contributes to heat gain.
- Internal heat losses: Infiltration of cold air and heat transfer through walls and windows cause heat loss.
- Ventilation requirements: Providing adequate fresh air for occupants’ health is crucial.
3. Equipment Selection:
After determining the load requirements, engineers select appropriate equipment like:
- Furnaces or boilers: Generate heat for the building.
- Air conditioners or chillers: Remove heat to cool the building.
- Air handlers: Process and distribute conditioned air.
- Ductwork or piping: Carry conditioned air or water throughout the building.
- Controls: Thermostats and control systems maintain desired temperatures.
4. System Design and Layout:
HVAC engineers design the system layout, considering factors like:
- Ductwork or piping configuration: Ensuring efficient distribution of conditioned air or water.
- Equipment placement: Optimizing equipment location for noise reduction, accessibility, and maintenance.
- Control system integration: Designing a control system to manage various equipment functions and ensure efficient operation.
5. Building Codes and Standards:
HVAC designs must adhere to relevant building codes and industry standards for safety, energy efficiency, and indoor air quality.
Software and Tools:
Modern HVAC design utilizes specialized software to perform complex calculations, model system performance, and create detailed drawings.
By following these steps, HVAC designers create systems that provide a comfortable, healthy, and energy-efficient environment for building occupants.