What is VAV in HVAC?
VAV stands for Variable Air Volume. It’s a type of HVAC system designed to deliver varying amounts of air to different zones within a building, depending on the cooling or heating needs of each specific area. This approach offers several advantages over traditional constant air volume (CAV) systems.
Here’s a breakdown of how VAV systems work:
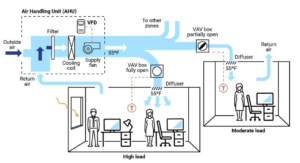
- Central Air Handling Unit (AHU): The AHU conditions the air (heating, cooling, dehumidifying) and supplies it to the building.
- Variable Airflow: Unlike CAV systems that deliver a constant airflow, VAV systems adjust the airflow based on the demand.
- Zone Control: Each zone (room, section of a floor) has a VAV terminal unit or VAV box with a sensor (usually a thermostat) that detects the temperature.
- Demand Response: The sensor in the VAV box sends a signal to the terminal unit, which adjusts a damper to regulate the airflow.
Benefits of VAV Systems:
- Improved Comfort: Provides more precise temperature control in different zones, leading to better occupant comfort.
- Energy Efficiency: By delivering only the necessary amount of air, VAV systems can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to CAV systems.
- Reduced Noise: Less overall airflow can lead to quieter operation of the HVAC system.
Here’s a table summarizing the key points:
| Feature | VAV System | CAV System |
|---|---|---|
| Airflow Delivery | Variable based on zone demand | Constant airflow throughout the building |
| Temperature Control | More precise control in each zone | Consistent temperature across the building |
| Energy Efficiency | More energy-efficient | Less energy-efficient |
| Noise Level | Potentially quieter operation | Potentially louder due to constant airflow |
However, VAV systems can also have some drawbacks:
- Complexity: Compared to CAV systems, VAV systems have more complex controls and require proper maintenance.
- Cost: The initial installation cost of a VAV system might be higher than a CAV system.



1 thought on “What is VAV in HVAC?”